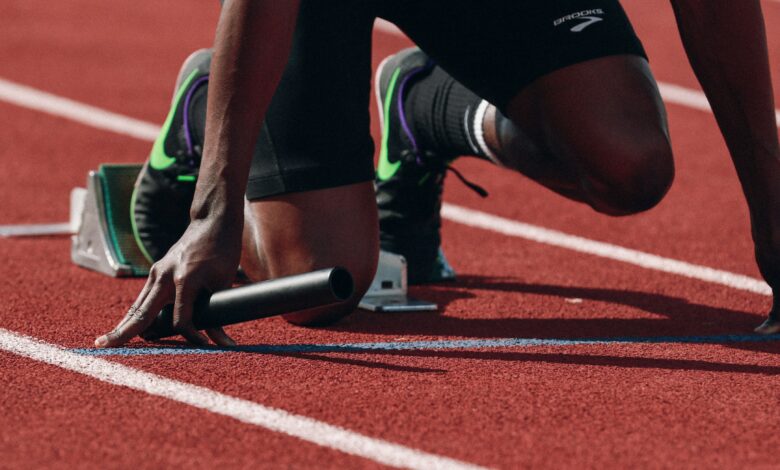
Sports have long been celebrated for their physical demands and the remarkable feats of endurance, strength, and agility they require. However, beneath the surface of every athletic performance lies a critical, often overlooked element: the mental game. Sports Psychology delves into the cognitive and emotional aspects of athletic performance, exploring how mental fortitude, focus, and resilience contribute to success. This article unpacks the intricate relationship between mind and body in sports, highlighting the significance of Sports Psychology in shaping athletic excellence.
1. The Foundations of Sports Psychology
Sports Psychology is a multidisciplinary field that combines principles of psychology, physiology, and kinesiology to understand and enhance athletic performance. At its core, Sports Psychology examines how mental and emotional factors influence athletes’ physical capabilities and overall performance. This field has evolved significantly over the past few decades, driven by the recognition that mental strength is as vital as physical conditioning.
The foundations of Sports Psychology are built on several key concepts, including motivation, confidence, focus, and resilience. Motivation drives athletes to set and pursue their goals, while confidence instills the belief that they can achieve these goals. Focus allows athletes to concentrate on the task at hand, and resilience helps them bounce back from setbacks. Together, these elements form the mental backbone that supports athletic success.
2. The Role of Mental Conditioning in Performance
Mental conditioning is a crucial aspect of Sports Psychology that involves training the mind to achieve peak performance. Just as athletes engage in physical training to enhance their strength and endurance, they also need to practice mental exercises to sharpen their cognitive skills. Techniques such as visualization, goal setting, and mindfulness are commonly used in mental conditioning.
Visualization is a powerful tool that allows athletes to create mental images of successful performances. By repeatedly visualizing themselves executing perfect plays or achieving their goals, athletes can build confidence and reduce anxiety. Goal setting involves establishing clear, achievable objectives that provide direction and motivation. Mindfulness, on the other hand, helps athletes stay present and focused, reducing distractions and enhancing concentration.
Mental conditioning also includes managing stress and anxiety, which are common challenges in competitive sports. Techniques like deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and cognitive-behavioral strategies can help athletes stay calm under pressure and maintain their composure in high-stakes situations.
3. The Impact of Emotional Intelligence on Athletic Success
Emotional intelligence, the ability to recognize, understand, and manage emotions, plays a significant role in Sports Psychology. Athletes with high emotional intelligence are better equipped to handle the emotional demands of competition, such as dealing with pressure, managing frustration, and maintaining a positive mindset.
Self-awareness, a key component of emotional intelligence, allows athletes to recognize their emotional states and understand how these emotions impact their performance. For instance, an athlete who is aware of their anxiety before a game can use relaxation techniques to calm themselves, preventing their nerves from affecting their performance.
Self-regulation, another aspect of emotional intelligence, involves managing emotions effectively. Athletes who can regulate their emotions are less likely to be derailed by negative feelings and are better able to stay focused and motivated. Social skills, including communication and teamwork, are also crucial for success in team sports, where collaboration and mutual support are essential.
Coaches and sports psychologists often work with athletes to develop their emotional intelligence, helping them build stronger relationships with teammates, handle conflicts constructively, and maintain a positive and resilient mindset.
4. The Psychology of Injury and Recovery
Injuries are an inevitable part of sports, and their impact extends beyond the physical realm. The psychological effects of injuries can be profound, affecting an athlete’s confidence, motivation, and overall well-being. Sports Psychology plays a critical role in helping athletes cope with injuries and navigate the recovery process.
One of the primary psychological challenges of injury is dealing with the loss of identity and purpose. Athletes often define themselves by their sport, and an injury can threaten this identity, leading to feelings of frustration, sadness, and even depression. Sports psychologists help athletes redefine their goals and find new sources of motivation during their recovery.
Mental strategies are also essential for overcoming fear and anxiety associated with returning to play. Athletes may fear re-injury or doubt their ability to perform at their previous level. Through techniques like visualization, positive self-talk, and gradual exposure, sports psychologists help athletes rebuild their confidence and reduce anxiety.
Additionally, maintaining a positive mindset during rehabilitation is crucial. Setting short-term, achievable goals can provide a sense of progress and accomplishment, helping athletes stay motivated throughout their recovery journey. Support from coaches, teammates, and mental health professionals also plays a vital role in an athlete’s psychological recovery.
Conclusion
Sports Psychology is an integral component of athletic success, providing athletes with the mental tools they need to excel. From the foundations of mental conditioning to the development of emotional intelligence and the management of injury and recovery, Sports Psychology addresses the cognitive and emotional aspects that underpin peak performance. By embracing the principles of Sports Psychology, athletes can enhance their focus, resilience, and overall mental strength, ultimately leading to greater achievements in their sports. As the field continues to evolve, the importance of the mental game in athletics becomes increasingly clear, underscoring the need for a holistic approach to training that integrates both physical and psychological elements.