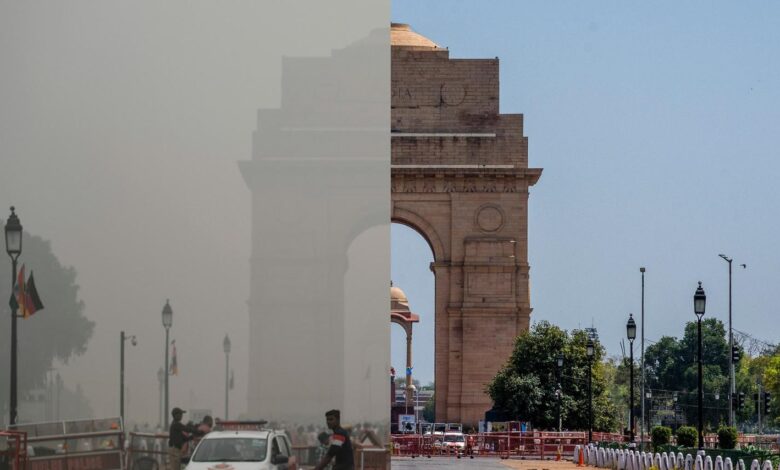
Despite further deterioration in the air quality of the National Capital Region, the authorities sealed Phase II of the Graded Response Action Plan that is meant to address alarmingly high pollution levels which peak during winter. The Air Quality Index more than frequently crosses 300 meaning “very poor” air quality. Several critical measures for redressing this significant environmental crisis are initiated by the government.
Understanding GRAP
The Graded Response Action Plan is the multi-step framework to curb air pollution in the Delhi-NCR region. The Graded Response plan categorized phases of pollution into different phases that elicit different responses based on the AQI measures taken to the highest level if the AQI exceeds 300. Phase II initiates emergency responses to alleviate intense smog covering the region.
Major Initiatives Under GRAP II
- Construction and demolition work: The most direct step is to immediately stop all construction and demolition works in the NCR. Construction sites are one of the major sources of particulate matter and various pollutants. This would put an end to such activities at least for a temporary period to give relief from air pollution.
- Prohibition of diesel generators: Except for hospitals, health units, telecommunication, etc., diesel generators are banned. Diesel generators emit high particulate matter and NOx; this is one of the major steps taken towards reducing harmful emissions.
- Traffic Management: Although there is certain restriction on the use of vehicles, the government has planned the odd-even scheme that will regulate the usage of vehicles with a check on the number of the license plates. This can be significantly reduced vehicular emissions as this is also one major cause of air pollution in urban areas.
- Increased Inspections Authorities increase air quality monitoring along with putting enforcement rules into place. They will place them at the construction sites to inspect for illegal use of generators.
- Public Educations Campaigns: The government also envisions taking measures that will be accompanied by educative campaigns targeting the public at sensitizing them on issues of pollution and health effects. The government urges the citizens to have less outdoor activities especially when there is a high level of pollution; however, it advises them on mask usage and air filters.
Weather Conditions Affecting Air Quality
The present dominant weather is an extremely crucial feature that results in aggravating the pollution levels in Delhi. Among the important meteorological variables contributing to this critical situation, the following are noted:
Temperature Inversions:
The prevalence of temperature inversions during the winter season traps the pollutant emissions close to the ground surface, thereby hindering its dispersion. This is one particular phenomenon more disturbing as it amasses the harmful particulate matter in the atmosphere.
Low Wind Speeds:
Lower the possibility of dispersion of pollutants due to low wind speeds, and thus the concentration level of harmful substances in the air faced becomes much more.
Crop Residue Burning:
Seasonal burning of crop waste by neighboring states is the critical main factor responsible for the present air quality crisis in Delhi. Efforts by the govt to curb this cannot carry effective policies, and therefore are not adequately effective in harvest times.
Humidity Levels:
Under high levels, water vapor may combine with the particulate matter to form severe smog that deteriorates air quality and visibility.
Health Implications
These adverse effects of poor quality air go back way in the past and are impressive in terms of reach. Exposure to higher levels of air pollutants can lead to health issues with conditions of respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and worsening of underlying diseases, such as asthma, depending on the intensity and duration of exposure. The vulnerable sections are children, the elderly, and disease-specific patients who are significantly affected. Health agencies strongly recommend that conditions need to be minimized while staying outdoors, use of air purification devices, and masks need to cut down on the unpleasant effects of pollution.
Conclusion
Implementation of GRAP II is an important step to redress the crisis of continuous pollution in Delhi and NCR. While the government enforces these measures, the lack of cooperation and perhaps an increase in awareness among the public will prove critical in fighting this menace of air pollution substantially. With threatening weather conditions foreseen for the next couple of weeks, continued efforts and community engagement will be critical in saving the health of the people by improving the quality of air. With joint efforts of residents and authorities, the region would be cleaner, healthier, and carbon pollutant-free ideas that will really bring in the much-needed fresh air in fighting head-on the challenges of air pollution brought about by urgent dilemmas.