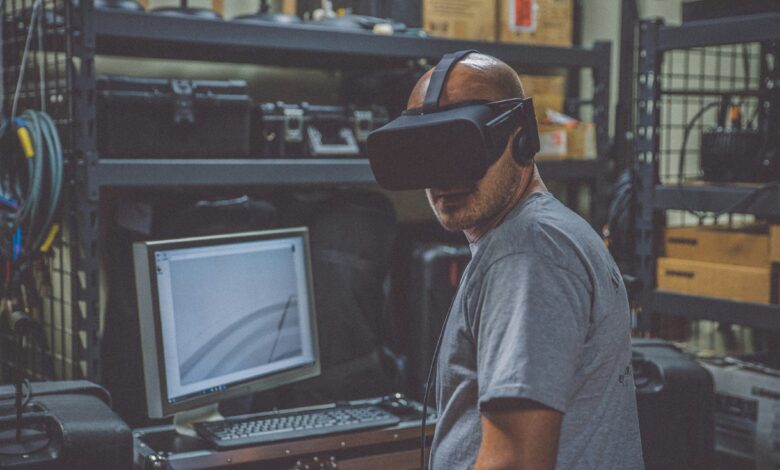
Virtual Reality (VR) has transcended beyond its initial niche into a mainstream phenomenon with vast applications across various industries. As technology continues to evolve, Virtual Reality is poised to revolutionize how we interact with digital environments, offering immersive experiences that were once confined to the realm of science fiction. In this article, we’ll explore the emerging trends and technologies shaping the future of Virtual Reality, and what we can expect from this rapidly advancing field.
1. The Evolution of Virtual Reality Hardware
The hardware used in Virtual Reality experiences has seen significant advancements, moving from bulky, wired setups to sleek, wireless headsets. One of the most promising trends is the development of lightweight, comfortable headsets that offer higher resolution displays and more precise motion tracking. Companies like Oculus, HTC, and Sony are leading the charge, continuously improving their products to provide more immersive and realistic experiences.
A notable advancement is the inclusion of eye-tracking technology in newer VR headsets. Eye-tracking allows for more natural interactions within the virtual environment, enabling users to make selections or navigate menus with just a glance. This technology also opens the door for foveated rendering, a process where the system only fully renders the part of the scene the user is looking at, thus conserving computing resources and allowing for higher graphical fidelity.
Another exciting development is the advent of haptic feedback systems, which provide physical sensations to the user. These systems can simulate textures, impacts, and other tactile experiences, making the virtual world feel more tangible. Companies are also exploring the potential of full-body haptic suits and gloves, which could one day allow users to feel virtual objects as if they were real.
2. Expanding Applications Beyond Gaming
While gaming remains a significant driver of Virtual Reality adoption, the technology’s potential extends far beyond entertainment. In healthcare, Virtual Reality is being used for surgical training, pain management, and therapy. For example, VR can create realistic simulations of medical procedures, allowing surgeons to practice in a risk-free environment. It has also been shown to help patients with chronic pain by providing immersive distractions that reduce discomfort.
In education, Virtual Reality offers an engaging and interactive way to learn. Virtual classrooms can transport students to historical events, scientific environments, or even outer space, providing a level of immersion that traditional methods cannot match. Additionally, VR can facilitate language learning by immersing students in virtual environments where they can practice speaking and listening in real-world scenarios.
The corporate world is also embracing Virtual Reality for training and collaboration. Companies can use VR to create realistic simulations for employee training, such as customer service scenarios or hazardous work environments. VR also enables remote collaboration, allowing teams from around the world to meet in a virtual space, share ideas, and work on projects as if they were in the same room.
3. Social Virtual Reality and the Metaverse
One of the most exciting frontiers for Virtual Reality is the concept of the metaverse—a shared, persistent, virtual space that is accessible to anyone with a VR headset. The metaverse aims to be a fully immersive digital world where users can interact, socialize, work, and play. While the idea has been around for decades, recent technological advancements are making it more feasible than ever.
Social Virtual Reality platforms like VRChat and Rec Room are already providing glimpses of what the metaverse could look like. These platforms allow users to create avatars, explore virtual worlds, and interact with others in real time. The potential for social interaction in Virtual Reality is immense, offering a new way for people to connect, regardless of physical location.
The development of the metaverse also raises questions about digital ownership and commerce. As virtual economies grow, there will be opportunities for businesses to sell digital goods and services. Blockchain technology and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) could play a crucial role in establishing ownership and scarcity in the virtual world, creating a new digital economy.
4. Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its potential, the widespread adoption of Virtual Reality faces several challenges and ethical considerations. One major concern is accessibility. High-quality VR hardware and experiences can be expensive, creating a barrier to entry for many users. As the technology becomes more affordable, it will be essential to ensure that everyone can access and benefit from Virtual Reality.
Another concern is the potential for addiction and overuse. The immersive nature of Virtual Reality can make it highly engaging, leading some users to spend excessive amounts of time in virtual worlds. This raises questions about the impact on mental health and the importance of setting boundaries between virtual and real life.
Privacy and data security are also significant issues in the realm of Virtual Reality. VR systems collect a vast amount of data about users, including their physical movements, eye tracking, and even biometric information. Ensuring that this data is protected and used ethically is crucial as the technology continues to develop.
Conclusion
The future of Virtual Reality is full of exciting possibilities, from groundbreaking hardware advancements to new applications in education, healthcare, and beyond. As the technology continues to evolve, it will reshape the way we interact with digital content and with each other. While there are challenges and ethical considerations to address, the potential benefits of Virtual Reality are immense. As we move towards a more immersive digital future, Virtual Reality will play an increasingly central role in our lives, offering experiences and opportunities that were once unimaginable.